ADSL high speed
telephone internet connections, uses a special modem, separate
line, faster than cable on dedicated line, must be within a prescribed
distance from a telephone switching stations (about 3K)
receives.
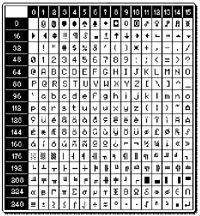
ASCII: American Standard Code for Information
Interchange
This is the standard method for encoding characters as 8-bit sequences of
binary numbers, allowing a maximum of 256 characters. Text files are
customarily called ASCII files.
ad banner
a.k.a. banner ad
AVI: Audio Video Interleave
This is a Windows platform audio and video file type, a common format for
small movies and videos. A 20-second movie clip in .avi format could be
as much a 3MB in size.
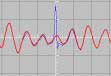
Analogue Electronics
Can create a signal with an infinity of voltages as opposed to Digital
electronics that has only 2 voltages On (HI) and Off (Lo).
A phonograph
LP recording (scratch) is analogue while a CD is digital.
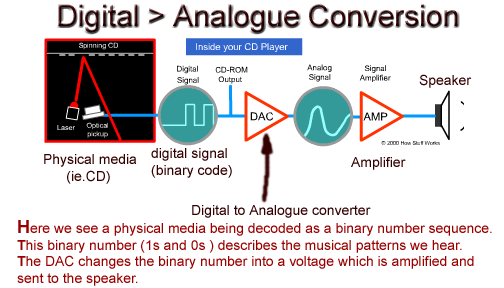
Analogue to Digital conversion A/D - analogue signals such
as sound or light (infinite variations) are converted into digital code
for storage or sending across the internet or space.
Anti Aliasing
Smoothing the jaggy edges of a selections or drawing/painting tools in
digital graphic arts.
Banner
An advertisement on a Web page, it links to another Web site or buffer
page. Ad banners are the most common unit of advertising on the Web and
cost anywhere from free to $5,000 to more than $150,000 per month
depending on the amount of traffic and page views the Web site (and thus
the ad banner)
Bandwidth
This refers to the difference, measured in Hz, between the highest and
lowest frequencies of a transmission. Most people loosely refer to
bandwidth as the amount of data that can be transferred over a network
connection.
Baud rate
This is a unit used to measure the number of data bits a modem can
transfer in one second. One baud is how many signals a modem can handle
in one second. Information is measured in bits, and bits come in the
signal. Higher baud modems can send and receive more signals in one
second, and the faster speeds also cram more bits into a signal.
BinHex: BINary HEXadecimal
This is a method of converting non-text, non-ASCII into ASCII. This is
necessary because Internet e-mail can only handle ASCII.
Bit
One piece of digital information. A byte = 4 bits. A bit is a 1 or a 0 .
Bitmap
.BMP is a file format for storing digital raster images. Each pixel is
define as a colour and a location.
Binary System a method of counting using
base 2 hence the numbers 0 or 1 that is represented in elelctronic terms
as Hi or Lo or On or Off
Bluetooth
An
open
technology specification for short-range radio links between mobile
PCs, "smart"
devices, and other portable machines. It is a networking technology that
enables data to easily transfer from one device to another, and unlike
infrared
(which requires a clear line of sight to operate properly), Bluetooth
operates over a 2.4 gigahertz radio frequency that allows communications through obstacles over distances of 30 feet. This means,
for example, that if this technology is combined with
MP3, your audio
could follow you from your living room to your car to your office. The
same data (your preferred songs) could get transferred to different
devices (your home stereo, your car radio, and your office audio system).
You could also use your phone to create a wireless Internet connection
for your laptop.
communications through obstacles over distances of 30 feet. This means,
for example, that if this technology is combined with
MP3, your audio
could follow you from your living room to your car to your office. The
same data (your preferred songs) could get transferred to different
devices (your home stereo, your car radio, and your office audio system).
You could also use your phone to create a wireless Internet connection
for your laptop.
Bluetooth is a global
wireless
standard,
and it eliminates the need for cords, thus allowing friends and business
associates to exchange contact information much more easily. Building on
the convenience of using a
LAN for file
and printer sharing, the creators envision a Bluetooth-enabled home,
where the appliances talk to each other using you as the antenna.
(Wouldn't you want your datebook to check your refrigerator to be sure
there's enough orange juice for Sunday brunch?
Browser
A browser is a program used to view, download, upload, surf or otherwise
access pages on the World
Wide Web.
Browsers access
servers and read HTML pages to translate the code into what we see. The
final product is referred to as a rendered Web page.
Netscape and Microsoft Internet Explorer and are examples of Web browsers. The program
you are using right now to view this information is called a browser.
Bug
A bug is a programming error that causes a program or computer system to
perform erratically, produce incorrect results or crash. The term bug was
coined when a real insect was discovered to have fouled up one of the
circuits of the first electronic digital computer, the ENIAC.
Cable - a type of communications wire called
coaxial designed to transmit TV to homes has been adopted as an Internet
medium for High Speed data traffic.
The limitation of cable is the fact that whiloe you are connected (almost
always) you are on the same IP address ........ thios makes it easier for
hackers to get into your computer or home network.
Cache
A cache temporarily stores information from a page in your computer. If
you request a page that is stored in a cache, your browser retrieves the
page from the cache more quickly than it could from its location on the
network.
Sometimes you may not want a page to be retrieved from a cache. The page
you brought initially may no longer be identical to the page currently
offered by the network. If a modification to a particular URL has
occurred, you may want the updated page rather than the now stale copy.
You can modify your cache preferences in Netscape under Edit >
Preferences > Advanced > Cache. Internet Explorer users should go to View
> Internet Options > Temporary Internet Files > Settings.
CCD
The light sensitive element that has replaced film in digital cameras.
CDR
A rewrite type CD
Colour Cast ----- appears when an image
appears to be cast from particular colour as if a filter was applied
CDROM Non rewriteable digital information
storage disc developed by Sony and Philips electronics in the early
1980's. electronics in the early
1980's.
CGI: Common Gateway Interface
This is the standard for running programs on a server from a Web page.
Gateway programs, or scripts, are executable programs that can be run by
themselves. They have been made external programs in order to allow them
to run interchangeably under various information servers. Gateways
conforming to this specification can be written in any language that
produces executable files. Some of the more popular languages include: C
or C++, Perl, Python, TCL and shells.
Chat
This is another term for Internet Relay Chat.
Client
In Internet terms, it's an application that performs a specific function,
such as Telnet or FTP. It's the front-end to an Internet process. In more
general terms, a client is a computer system or process that requests a
service of another computer system or process. The much talked about
client-server architecture refers to a workstation requesting the
contents of a file from a server. that are disabled or inaccessible.
CMYK Cyan
Magenta Yellow
Black are the colours used in the subtractive colour system
used in printing such as inkjets and dye sublimation printers.
Colour Bit Depth
1bit = black + white
8bit
256 bit B/W = Greyscale
24 bit colour can generate 16.7 million colours (photorealistic) your
eyes can perceive 10 million colours
Compression
To make a file smaller such as in SAVE to WEB in PhotoShop or ZIP etc.
A .JPG image file can various level of compression and the image quality
will be a reflection of the level of compression.
Cookie
A cookie is something that you clicked on while using the Internet. The
cookie is stored in a text file on your hard drive. This information is
usually accessed by a server when you connect to a Web site that requires
some information about you or your system. As a user, you log into a
system by entering your username and password. A text file is then saved
by your browser for later access. This occurrence is called "handing a
cookie." It prevents you from having to log in again if you happen to
leave the Web site and return later. Cookies are also used in the process
of purchasing items on the Web. By saving user information to a text file
as someone moves through a shopping Web site, the user can later go to an
order form and view all of the items that they have selected. Web site that requires
some information about you or your system. As a user, you log into a
system by entering your username and password. A text file is then saved
by your browser for later access. This occurrence is called "handing a
cookie." It prevents you from having to log in again if you happen to
leave the Web site and return later. Cookies are also used in the process
of purchasing items on the Web. By saving user information to a text file
as someone moves through a shopping Web site, the user can later go to an
order form and view all of the items that they have selected.
Cyberspace
This is the "world of computers and the society that gathers around
them," as referred to by William Gibson in his fantasy novel Neuromancer.
It now loosely refers to the online world and even more loosely to the
Internet.
Download
This means to copy data, usually an entire file, from a main source to a
peripheral device. The term is often used to describe the process of
copying a file from an online service to one's own computer.
Contrast The range of tones in an image
between a highlight and a shadow.
CPU the central processing unit of a
computer ( the brain )
Digital Electronics a system a that use 2
states on - off / hi - lo / 5Volts - 0 volts
analogue signals (infinite variation) are sampled at many times a second
and the analogue voltages
are converted to a digital number and stored in digital storage media.
Later the digital signal is changed back to an analogue system for human
sensing.
D/A conversion -- occurs when a binary (1/0's) signal is
changed back to an analogue (real world) signal.
An example is when you
play a CD
Download as opposed to upload a file is
received by the client ( your computer ) from the server the remote host
computer where the file is resident.
Digital Zoom - as opposed to optical zoom
the camera uses a programme to enlarge the pixels resulting in an
enlarged image with reduced quality.
DPI dots per inch
set your internet images for 72 or 96 DPI
set your print images to 300 0r 600 dpi
DPOF digital print order format used to mark digital images for
processing at retailers like Blacks or Henry's
Driver
software that tells a computer how to operate a remote device such as a
printer or webcam or printer.
DVD - is the new generation of optical disc storage technology. DVD
is essentially a bigger, faster CD that can hold cinema-like video,
better-than-CD audio, still photos, and computer data. DVD aims to
encompass home entertainment, computers, and business information with a
single digital format. It has replaced laserdisc, is well on the way to
replacing videotape and video game cartridges, and could eventually
replace audio CD and CD-ROM. DVD has widespread support from all major
electronics companies, all major computer hardware companies, and all
major movie and music studios. With this unprecedented support, DVD
became the most successful consumer electronics product of all time in
less than three years of its introduction. In 2003, six years after
introduction, there were over 250 million DVD playback devices worldwide,
counting DVD players, DVD PCs, and DVD game consoles. This was more than
half the numbers of VCRs, setting DVD up to become the new standard for
video publishing.
http://www.dvddemystified.com/dvdfaq.html#1.1
EVF - electronic (eyeball) viewfinder often found on digital still
and video cams
Exposure - the amount of light that falls on the CCD of a digital
camera
exposure is controlled by the the
A) aperture (opening to the camera)
B) shutter speed (the shutter opens and closes to allow light to pass by
the lens an aperature to the CCD (film in a regular camera)
Electronic Mail: e-mail
This is a method by which computer users can exchange messages with each
other over a network. E-mail is probably the most widely-used
communications tool on the Internet. There are many quirky conventions to
e-mail, but most entail a "To:," a "From:" and "Subject:" line. One of
e-mail's advantages is its ability to be forwarded and replied to easily.
Encryption
This is the basis of network security. Encryption encodes network packets
to prevent anyone except the intended recipient from accessing the data.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
FAQs are widely available on the Internet and usually take the form of
large, instructional text files. They are written on a wide variety of
topics and are usually the most up-to-date source for specialized
information.
Feathered edge
a soft edge created by a fading away of the light intensity from the edge
..... use it allot of pro results
Firewall - software used block hacker
invasions on a web connected computer
Fire wire - a wired input to your computer
for the fast transfer of large (usually image files)
- a MAC invention so standard on a MAC add on to a PC
- essential for digital video editing
Fixed Lens ( can't optically zoom)
Flash Memory a fast memory chip that can
remember all the data even when the power is turned off
Memory Sticks, Compact Flash, MultiMedia Cards, Olympus xD Picture Cards
used in MP3 players Pocket computers, and Digital Cameras. players Pocket computers, and Digital Cameras.
Freeware
Freeware is... free, just as you'd imagine it! The software was developed
just for the sake of providing you, the end user, with a cool new
application. If you really like the program, you might take a moment to
send the author a thank you note, but there are no strings attached to
these programs.
FTP: File Transfer Protocol
This is the most widely-used way of downloading and uploading files
across an Internet connection. The File Transfer Protocol is a
standardized way to connect computers so that files can be shared between
them easily. There is a set of commands in FTP for making and changing
directories, transferring, copying, moving and deleting files. Formerly,
all FTP connections were text-based, but graphical applications are now
available that make FTP commands as easy as dragging and dropping. FTP
clients exist for a number of platforms.
GIF: Graphics Interchange Format
This format was developed by CompuServe using compression technology from
Unisys. On the World Wide Web, pictures and graphics that you see on Web
pages are usually in GIF format because the files are small and download
quickly.
Hacker
This is a computer user who works to understand the ins and outs of
computers, networks and the Internet. Hackers are generally benign and
believe that information should be free. the Internet. Hackers are generally benign and
believe that information should be free.
Hard Drive the main memory centre in your
computer. 
Home Network - a homenetwork can be configured by connecting your cable
modem to a hub or router and then splitting off from there to other
computers (usually 4 allowed ) on Cat. 5 network cable or better still to
a wireless switch to computers equipped with wireless network adapters
Interpolation -- when you stretch an image
the computer has to interpolate for missing information and thus lowers
the image quality (pixelation) blocky squares.
Instant Messaging
This is a type of communications service that enables you to create a
private chat room with another individual. Typically, the instant
messaging system alerts you whenever somebody on your private list is
online. You can then initiate a chat session with that particular
individual.
MSN is an instant messenger
Internet
The Internet is a globally linked system of computers that are logically
connected based on the Internet Protocol (IP). The Internet provides
different ways to access private and public information worldwide.
IP: Internet Protocol
Intranet
This is a private network, inside a company or an organization, that uses
the same kinds of software that you would find on the public Internet.
The difference is that an intranet is only for internal use. As the
Internet has become more popular, many of the tools used on the Internet
are being used in private networks. For example, many companies have Web
servers that are available only to employees.
ISDN: Integrated Services Digital Network
ISDN technology combines voice and digital network services in a single
medium. ISDN makes it possible for communications carriers to offer their
customers digital data services as well as voice connections through a
single line. CCITT defines the standards relating to ISDN.
Jaggies --- those white pixels around an
image that has been cut out and imported ........ prevent this by
creating a matt in the SAFE for WEB function.
JPEG: Joint Photographic Experts Group
This is one of the two most common types of images used on the World Wide
Web, the other being GIF. JPEG is named after the Joint Photographic
Experts
Logic> digital electronic systems use a 2
state binary system to compute information ..... its lucky that computers
can work at high speeds because it is a rather unwieldy system.
As well as binary numbers (0 or 1) digital systems use a philosophical
system called logic and truth tables. Electronic gates constructed of
transistor switches are used as follows
AND all
inputs Hi output high
OR
one of 2 or more inputs high output goes high
NOT if input is Hi the output is inverted to a Lo
as odd as it seems all of digital electronics is based on logic as
described by a few basic logic gaes, ...... fortunately the computer
works quickly (high speed idiot)
Link Hypertext
A link is a text or an image area on a Web page that a user can click on
to connect to or reference another document. Links can connect several
kinds of documents. Most commonly, links are thought of as what connects
two Web pages or Web sites.
LCD a type of screen that uses liquid
crystal pixels ....... like your calculator
Lossy a type of image file that results in a
loss of data such a compressed files like JPG
TIFF and RAW file formats are not lossy but the file sizes are huge
compared (30- 50 mB!)
Macro a camera setting that allows you to
take close up pictures 15cm and closer.
Marquee --- the outline of dots that
surround a cut/selected digital image
Marshall McLuhan Canadian
Media Guru - the rest of the world is just now catching up to his
wisdom regarding the impact of media on human ideosphere
"The Global Village "
"Art is anything you can get away with."
"Publication is a self-invasion of privacy."
"There are no passengers on Spaceship Earth. We are all crew."
"Advertising is an environmental striptease for a world of abundance.
"Ads are the cave art of the twentieth century."
"Turn on, tune in, drop out"
Mega Pixel a camera that develops over 1
million pixels of information on the CCD light sensor of a digital
camera.
MPEG: Motion Picture Experts Group
MPEG is a type of audio or video file that is commonly found on the
Internet. In order to hear or see an MPEG movie, you will need to install
a helper application or a Web browser plug-in. MPEG is an algorithm for
compressing audio and video; it is not to be confused with Motion-JPEG.
Modem
Modem means modulate/de-modulate because that's exactly what it does with
a signal. A modem is a piece of hardware, either internal or external,
that allows your computer to connect to other computers. You can also
send faxes and make data connections and voice connections if your type
of modem supports it. To change from ANALOGUE to DIGITAL
MP3: MPEG-1, Layer 3
MPEG-1, Layer 3 is an amazing standard for audio compression. It is
capable of 10:1 compression with little loss in quality. An audio sample
at CD Quality (44KHz, 16 bit, Stereo) takes up 172KB for every second
with a standard WAV Audio file. MP3 compression takes only 16KB per
second when compressed at the standard bit rate of 128Kbps. By
compressing at lower bit rates, MP3s can be lowered to 12KB per second
with some quality loss.
MUD: Multi-User Domain
Multimedia
This is the use of computers to present text, graphics, video, animation
and sound in an integrated way.
Network ---- 2 or more computers and
peripherals are tied together as a functional unit your computer is part
of a giant global network when connected to the Internet.
Netiquette
A combination of the words "'Net" and "etiquette," this refers to proper
behavior on a network, and more generally, the Internet. The key element
in Netiquette is remembering that actual people are on the other end of a
computer connection, and offensive comments or actions are just as
offensive, even if you can't see the recipient. Other rules of Netiquette
include not wasting bandwidth or other users' time. For instance, sending
unsolicited e-mail attachments constitutes bad Netiquette.
Network
A network is two or more computers that are connected. The most common
types of networks are:
· LAN, local area network:
The computers are in close proximity to one another. The are usually in
the same office space, room or building
· WAN, wide area network:
The computers are in different geographic locations and are connected by
telephone lines or radio waves.
the wealth of data that Usenet contains.
Peripheral --- a device connected to a
computer such as a printer or camera/scanner/
POP: Post Office Protocol
This is a protocol designed to allow individual users to read mail from a
server. There are three versions: POP, POP2 and POP3. When e-mail is sent
to you, it is stored on the server until it is accessed by you. Once you
are authenticated, the POP is used to transmit the stored mail from the
server to your local mailbox on your client machine.
Protocol
Protocol, put simply, is the "language" spoken between computers to help
them exchange information. More technically, it's a formal description of
message formats and rules that two computers must follow to exchange
those messages. Protocols can describe low-level details of
machine-to-machine
Pixel -- picture / element = pixel the small
units of image that you seen in print or on the computer monitor.
PNG 8 / PNG 24
portable networks graphics digital image file format
RAM
random access memory the chip(S) that store information that the CPU is
currently working with increases in RAM will always speed up the
performance of a computer especially when working with graphics intensive
programmes such as PhotoShop.
RGB colour system uses 256 levels of each of
the additive primary colours to define colours digitally
since digital use a 2 bit system there are a possible 2 to the power of
256 or 25 million colours available more than the human eye can perceive.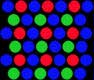
WHITE = 256 256 256
or in hex ff ff ff
BLACK = 000 000 000 or in hex 00 00 00
GREEN = 000 xxx 000
etc and all the many combinations!!!
Removable media ------ flash cards / cds /
floppies from cameras MP3 players
Resolution
The amount of digital information in a digital image (how grainy a
picture looks) the higher the resolution the better most images will
appear and the larger the image file.
640x480 pixels = about 50 Kb file sizes.
Saturation to increase the intensity of the
primary colours in and image use the sponge tool in Photoshop to
Increase/decrease the saturation level of an image

Search Engine
This is a program that searches one or more documents for specified
keywords and returns a list of locations where those keywords were found.
Although search engines are really a general class of programs, the term
is often used to specifically describe systems like Alta Vista and Excite
that enable users to search for documents on the World Wide Web and in
USENET newsgroups.
Selection tool - lasso, magnet, magic wand
are all tools used to select and mask parts of an image that will be
surrounded by a marquee line
Shareware
This is software that you can download, try and decide whether or not
it's right for you. If you like it, you pay a nominal fee for the
full-featured program. If you don't want to keep it, shareware programs
usually either stop functioning after a period of time or they continue
to work but will never have all of the features that the purchased
version would have.

Sir Sandford Fleming (Canadian)
- Proposed the present system of standard time, by which the world
is divided into 24 equal time zones and a telegraph communication cabling
system that connected all of the British Empire that was completed in
1902.
Shutter Speed will determine along with the
aperture amount of light exposure the CCD will receive when taking a
digital image.
Taking the image of a moving object with a slow shutter speed will create
a lighter image and the subject will be blurred due to timed exposure
over the traveled distance while the shutter was open
Sports/wildlife photography uses high shutter speeds
Subject modes/Scene modes ----- special
situation automatic digital camera settings
- they are usually set ups for twilight , night ,
interior lighting , etc. scene modes are great for automated settings in
difficult settings.
Server
A server is simply a computer that provides resources, such as files or
other information. Common Internet servers include file servers and name
servers like the Domain Name Service to access the Internet. When you
upload (FTP) your files to the internet you are sending them to a server
which can serve them to a client.
Spam
This is the inappropriate use of a mailing list, Usenet or other
networked system. Spamming is sending the same message to a large number
of people who didn't ask for it. The term might have come from a famous
Monty Python skit that features the word "spam" over and over. The term
may also have come from someone's low opinion of the food product with
the same name, which is generally perceived as a generic content-free
waste of resources. Spam, the processed meat product, is a registered
trademark of Hormel Corporation.
Streaming
Streaming means that audio, video and text are made available for viewing
on your computer even as they are in the process of downloading to your
system from a Web site.
TIFF standard format for high-resolution
bitmapped graphics ( huge file sizes good for consumer product
advertisement pictures)
T1
This is a term used to denote the type of connection of a host to the
Internet. A T1 transmits a DS-1 formatted digital signal at 1.544Mbps.
T3
This is another term used to denote the type of connection of a host to
the Internet. A T3 transmits a DS-3 formatted digital signal at
44.746Mbps.
TCP/IP: Transmission Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol
TCP/IP is the standard communications protocol required for
Internet computers. To communicate using TCP/IP, PCs need a set of
software components called a TCP/IP stack. UNIX systems are built with
TCP/IP capabilities.
TWAIN technology without an independent name
------ a universal protocol to allow peripherals such as cameras and
scanners to connect to computers.
URL: Universal Resource Locator
More commonly referred to as the URL, the Universal Resource Locator is
the entire series that is recognized universally as the address for an
Internet resource. Each resource on the Internet has a unique URL. URLs
begin with letters that identify the resource type, such as http, ftp or
gopher. These types are followed by a colon and two slashes. Next, the
computer's name is listed, followed by the directory and
filename of the remote resource.
Upload
To upload means to transmit data from a computer to a bulletin board
service, mainframe or network.
Utility
This is a program that performs a very specific task, usually related to
managing system resources. Such as a virus checker
USB 1 universal serial bus port a fast wired connection to your
computer
USB 2 an even faster version of the above same connectors are used
Virus
This program replicates itself on computer systems by incorporating
itself into other program s that are shared among computer systems. s that are shared among computer systems.
WAV: Waveform Audio
This is the format for storing sound in files that was developed jointly
by Microsoft and IBM. Support for WAV files was built into Windows 95,
making it the de facto standard for sound on PCs. WAV sound files end
with a .wav extension and can be played by nearly all Windows
applications that support sound.
World Wide Web
The "Web" is a collection of online documents housed on Internet servers
around the world. The concept of the Web was created by researchers at
CERN in Switzerland. Web documents are written in HTML. To access these
documents, you have to use a Web browser like Netscape, Microsoft
Explorer or Mosaic. When these browsers access a page, the server uses
the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, or HTTP, to send the document to your
computer. The concept of the Web was created by researchers at
CERN in Switzerland. Web documents are written in HTML. To access these
documents, you have to use a Web browser like Netscape, Microsoft
Explorer or Mosaic. When these browsers access a page, the server uses
the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, or HTTP, to send the document to your
computer.
Worm
A worm is a computer program that replicates itself and is
self-propagating. While viruses are designed to cause problems on a local
system and are passed through boot sectors of disks and through files,
worms are designed to thrive in network environments.
Network worms were
first defined by Shoch & Hupp of Xerox in ACM Communications (March
1982).
The most infamous worm was the Internet Worm of November 1988. It
successfully propagated itself on over 6,000 systems across the Internet.
SInce then worms have been a constant problem.
White Balance ------ sets the digital camera
settings t compensate for a variety of indoo r and outdoor ligting
settings r and outdoor ligting
settings
Wide Angle Lens -----a short focal length lens that gives a wide angle of view and a long depth of focus.
ZIP
A Zip file is a Microsoft Windows-based compressed file. It can contain
several files and a directory structure. On the Internet, large graphics
and programs are usually compressed into ZIP files and then made
available for download. After you download this file, you need to use
decompression software program to "Unzip" the file. Several popular tools
exist for zipping: PKZIP in the DOS operating system, TurboZip Express,
WinZip and NetZIP in Windows, MacZip for Macintosh users, and Zip.
MS Harris
We are in the Age of Possibility
.....any thing is possible.
you are responsible for your experience.
A new Super Power is emerging ......... "the human race" it has
no need for the oligarchy the plutocracy or the clerics.
|



 communications through obstacles over distances of 30 feet. This means,
for example, that if this technology is combined with
communications through obstacles over distances of 30 feet. This means,
for example, that if this technology is combined with

 electronics in the early
1980's.
electronics in the early
1980's. Web site that requires
some information about you or your system. As a user, you log into a
system by entering your username and password. A text file is then saved
by your browser for later access. This occurrence is called "handing a
cookie." It prevents you from having to log in again if you happen to
leave the Web site and return later. Cookies are also used in the process
of purchasing items on the Web. By saving user information to a text file
as someone moves through a shopping Web site, the user can later go to an
order form and view all of the items that they have selected.
Web site that requires
some information about you or your system. As a user, you log into a
system by entering your username and password. A text file is then saved
by your browser for later access. This occurrence is called "handing a
cookie." It prevents you from having to log in again if you happen to
leave the Web site and return later. Cookies are also used in the process
of purchasing items on the Web. By saving user information to a text file
as someone moves through a shopping Web site, the user can later go to an
order form and view all of the items that they have selected. 

 players Pocket computers, and Digital Cameras.
players Pocket computers, and Digital Cameras. the Internet. Hackers are generally benign and
believe that information should be free.
the Internet. Hackers are generally benign and
believe that information should be free. 



 s that are shared among computer systems.
s that are shared among computer systems.  The concept of the Web was created by researchers at
CERN in Switzerland. Web documents are written in HTML. To access these
documents, you have to use a Web browser like Netscape, Microsoft
Explorer or Mosaic. When these browsers access a page, the server uses
the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, or HTTP, to send the document to your
computer.
The concept of the Web was created by researchers at
CERN in Switzerland. Web documents are written in HTML. To access these
documents, you have to use a Web browser like Netscape, Microsoft
Explorer or Mosaic. When these browsers access a page, the server uses
the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, or HTTP, to send the document to your
computer.  r and outdoor ligting
settings
r and outdoor ligting
settings