| 26) 89Sr
- has the
same valence number as calcium and will be incorporated in bone tissue if
available , unfortunately 90Sr is readily formed during above ground
nuclear blasts 27) Tc - the radiaoactive form can easily created in labs (hospitals) and is used as a radioactive tracer in nuclear medical diagnostics 28) Ag Cd Sn 29) Iodine 127 - is a key element in the production of the metabolic regulating hormone thyroxin iodine 131 can be produced and is used both to image (diagnostics) the thyroid gland and to kill overactive (hyperthyroid) or cancerous thyroid tissue ( therapeutics)
30) Ba - salts of Barium are
radio opaque and are used
to image the
G.I. tract
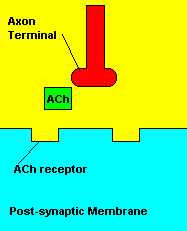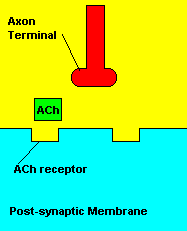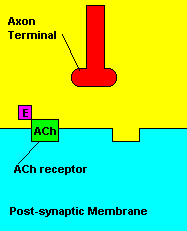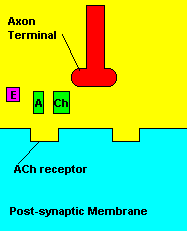
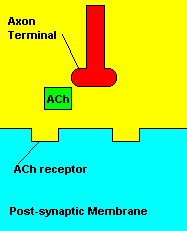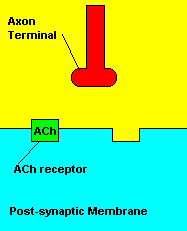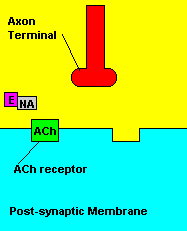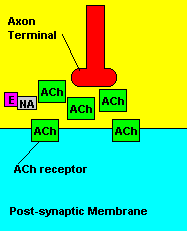
with X-rays The Acetylcholine Synapse
|