|
Miller Experiment
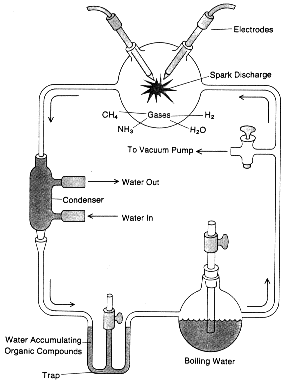 1956 1956
- Miller attempts to replicate (in vitro) conditions of the Early
atmosphere (H2O NH3, CH4, H2,
CO2)
- heat and high voltage electrical energy was applied to the closed
circuit
- in several days water samples revealed amino acids, nucleic acids,
complex molecules common to all life forms
- what does this prove?

Life's progress over time
> 3.6-3.7 billion years ago: appearance
of life
> 2.5 billion years ago oxygen-forming photosynthesis
> ~2.2 billion years ago: aerobic respiration
> ~1.5 billion years ago: first evidence of fossil eukaryotes
Precambrian
Era (simple
unicellular life, prokaryotes, low diversity, anaerobic life)
3.6-3.7 billion years ago: appearance of life anaerobic
heterotrophes
> likely first cells were anaerobic, heterotrophic bacteria
anaerobic = does not require free oxygen
heterotrophic = does not make its own food (primordial broth
supplies food)
> next step: anaerobic autotrophs
Were able to fix CO2 (take carbon from air)
turning CO2 + H into organic molecules
Hydrogen donors initially were H2, H2S
Energy sources for autotrophics >>>> Deep Sea Thermal Vent
Deep Sea Thermal Vent
> First used chemical energy from elements in surrounding medium
(primordial broth)
chemoautotrophs ( we see this in deep-sea vents today!)
> As this energy ran low, evolved ability to capture energy from light
> Photoautotrophs (primitive photosynthesis)
Life' s first major environmental crisis
(loss of H+ donors in primordial broth))
Available hydrogen donors (H2, H2S) used up quickly
(goodbye primordial broth)
Key innovation around 2.5 billion years
oxygen-forming photosynthesis (cyanobacteria)
Use of H2O as a hydrogen donor
Life' s second major environmental crisis
 Iron Banded Rock
Iron Banded Rock
Toxic O2 released into atmosphere
Most of the initial O2 was locked up by iron in the oceans and
soils (Banded iron formations) = rusting of Earth minerals
More O2 from water keep coming, leading to an O2
rich atmosphere
Aerobic respiration
endosymbiotic evolution of mitochondria led to aerobic respiration a
highly efficient system
allowed larger cells and the potential of multicellular organisms that
establish complex food webs within ecosystems
Cambrian Era (sudden appearance of
vast species diversity , eukaryotes)
- the Cambrian era started about 600 M Y ago dinosaurs died off 65 million
years ago
- human culture about 50K Y old
- scientific human culture about 250 Y old
want to know about geochronology visit
my
Earth Space Site
|