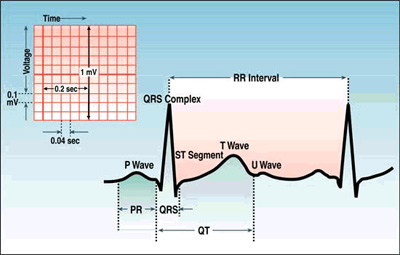
ECG Waves and Intervals:
How to read their meaning
> P wave: depolarization of the right and left
atria
> QRS complex: right and left ventricular depolarization
>ST-T wave: ventricular repolarization
> U wave: probably represents "afterdepolarizations" in the
ventricles
> PR interval: time interval from onset of atrial depolarization (P
wave) to onset of ventricular depolarization (QRS complex)
> QRS duration: duration of ventricular muscle depolarization due to
contraction of this large muscle mass
> QT interval: duration of ventricular depolarization and repolarization
> RR interval: duration of ventricular cardiac cycle (an indicator of
ventricular rate)
for more detail

ECG paper moves at a standardized 25mm/sec.
The vertical lines can be used to measure time.
There is a 0.20 sec between 2 of the large lines. Therefore, if you
count the number of heart beats (QRS complexes) in between 30 large
boxes (6 seconds) and multiply by 10, you have beats per minute.
Conveniently, ECG paper usually has special markings every 3 seconds so
you don't have to count 30 large boxes.
An easier and quicker way to estimate the heart rate is seen in the
diagram above, when QRS complexes are 1 box apart the rate is 300 bpm. 2
boxes apart...150 bpm, etc. So if you memorize these simple numbers you
can estimate the heart rate at a glance!
|

