|
Gel Electrophoresis separation technologies |
| What is it? -
a method used to separate proteins or genetic material that exists in a
mixture for purposes of ID both quantitative and qualitative. The word means "carried by electricity" and such is the case. The fragments of molecules are literally moved through an agarose or polyacrylamide gel (source of traveling resistance) by a force of electrical voltage (V). As the molecules move through the gel they travel at various speeds due to the size and electrical charge of each type of molecule. This causes them to travel in "fronts" that separate each type of molecule (gene, amino acid or protein). Procedure 1) equipment is setup > power supply, gel, wells for the mixtures are created in gel as starting point 2) mixtures are placed in the wells 3) power on 4) electrophoresis begins 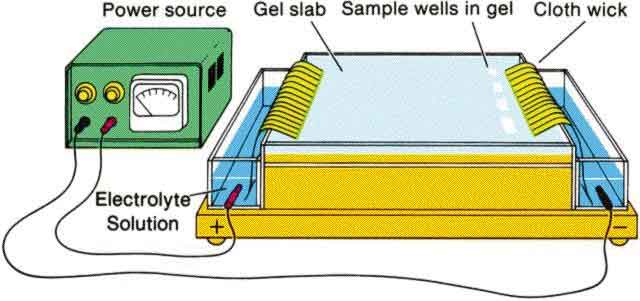 5) gel is treated (to visualize bands) and analyzed for the banding patterns   >
here is an example of the banding pattern that might be expected after the
electrophoresis has run for several hours >
here is an example of the banding pattern that might be expected after the
electrophoresis has run for several hours- smaller/lighter fragments travel further - other image enhancing techniques have been developed such as fluorescence , autoradiography (uses radioisotope tags), and computer recognition for batch processing - higher voltage = faster separation Other separation techniques in biology include centrifugation and chromatography |