| Before
cells divide (mitosis) they must duplicate their DNA this is a complex
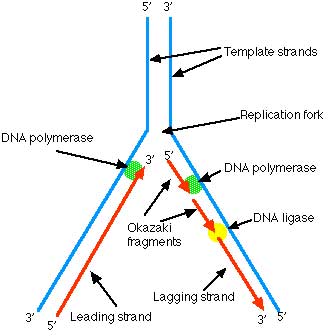
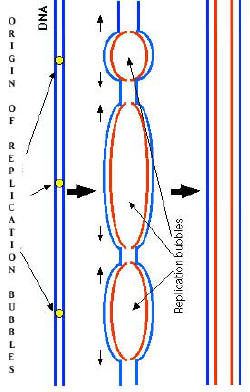
multi step process. This performed in the S phase of the cell cycle. Replication in eukaryotes occurs at numerous points along the Chromosome at replication "bubbles". The partial strands link up to form the full strand in time. 1) A portion of the double helix is unwound by a
helicase an enzyme that softens the DNA helix
opening it. 3) A molecule of a DNA polymerase binds to
one strand of the DNA 4) It begins moving along it in the 3' to 5' direction, using it as a template for assembling a leading strand of nucleotides and reforming one of the daughter double helix. In eukaryotes, this molecule is called delta DNA polymerase (δ). 5) Since DNA synthesis can only occur 5' to 3', a
molecule of a second type of DNA polymerase (epsilon, ε, in eukaryotes)
binds to the other template strand as the double helix 6) Epsilon DNA polymerase must synthesize
discontinuous segments of polynucleotides (called
Okazaki fragments) or fragments of DNA. 7) Another enzyme, DNA
ligase then stitches these together into the
lagging strand.
NEXT >>> |
Replication of DNA involves the semi conservative replication of
complimentary strand of DNA |
 next
next
next
next