|
Structure of
Nucleotides and DNA
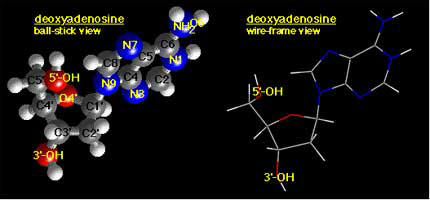 \ \
Note that the deoxyribose has a 3' and 5'
hydroxyl group these landmarks are used to orient the direction of the DNA
strands.
Deoxyribose is a 5 carbon sugar.
Note this 5
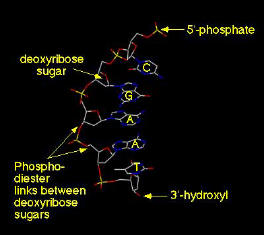 nucleotide (TAAGC)
single strand of DNA has a 5' and a 3' end. nucleotide (TAAGC)
single strand of DNA has a 5' and a 3' end.
Phosophodiester links join adjacent bases.
The twisting that creates a helix is caused by longitudinal HYDROGEN bonds
between bases.
The Helix twists through 360* every 3.4nm
Note that when the 2 sides of the DNA helix are
paired up they are antiparallel the
3'-5' ends are oriented in opposite directions.
The Double Helix
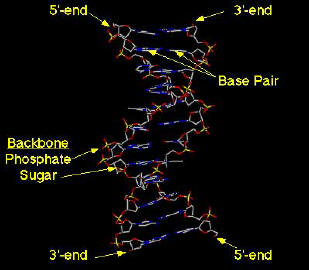 The
helix makes a complete turn every 3.4 nm . The
helix makes a complete turn every 3.4 nm .
Hydrogen bonds between the base pairs hold each strand of the helix
together laterally and also create a torque in the molecule that causes a
twisting helical shape to appear.
The structure of DNA allows for duplication by formation of a
complementary half. The H bonds between the 2 halves of the DNA strands
are strong enough to hold together and yet supple enough to be opened for
transcription and duplication.
The DNA molecule is elastic and supple yet can retain its integrity for
thousands of years in the suitable conditions.
next >
animation mitosis clik
here |
 \
\ nucleotide (TAAGC)
single strand of DNA has a 5' and a 3' end.
nucleotide (TAAGC)
single strand of DNA has a 5' and a 3' end. The
helix makes a complete turn every 3.4 nm .
The
helix makes a complete turn every 3.4 nm .