|
Symbiosis - a relationship
between populations of different species in close often intimate contact.
Recall - endosymbiontic evolution of mitochondria and chloroplasts |
|
|
Mutualism -
a symbiotic relationship where both
relationship species benefit. There are numerous cases of mutualism in nature that have arisen through the process of coevolution. This is where 2 species have evolved in conjunction in a way that creates strong often obligatory codependence. For example the bacteria in the gut of cows, they provide glucose from cellulose in the cow's diet and the cow supplies the food warmth and an anoxic environment. Cows as a result release significant volumes of methane contributing to global warming.
Lichens the leafy green plant like organism that
grows on rocks is actually a fungus and an algae living together
symbiotically. Neither the alga or the fungus can live with out each other Coral polyps
and algae are another good example and by the way if the coral algae dies
the coral bleaches and the
polyps die soon later. |
 Cow |
 Lichen |
|
 Coral |
|
|
Commensalism -
relationship between 2 species where only 1
species benefits and the other is not harmed. Some ant birds follow the trails of tropical fire ants because the ants scare up other organisms upon which its preys. Some Damsel Fish can hide among the normally stinging polyps of anemonae and coral polyps without being harmed and are protected by the polyps. |
 Antbird
|
|
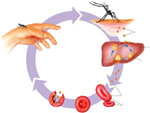
Parasitism -
parasites live in or on a host organism
which supplies it with nutrition and habitat. A well evolved parasite does
not cause the host great harm as it must count on the hosts survival for
its own. Many diseases and parasites of humans originated and continue to
originate in Africa where humans spent the most time coevolving with them.
One of the benefits of human migration north to the inhospitable northern
climes was the escape from these parasites and diseases although new and
old diseases soon followed.
Endoparasites
- (inside of body) the hookworm lives in the small intestine attached to
the |
|

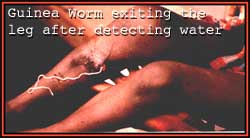 intestinal wall. The Guinea worm lives inside the leg of a human host and
intestinal wall. The Guinea worm lives inside the leg of a human host and protrudes out to lay eggs when the host contacts water. It must be removed
by twisting on a twig over a period of and it is believed this action is
displayed on the medical symbol the
caduceus.
protrudes out to lay eggs when the host contacts water. It must be removed
by twisting on a twig over a period of and it is believed this action is
displayed on the medical symbol the
caduceus.
